🔐 What is Encryption?
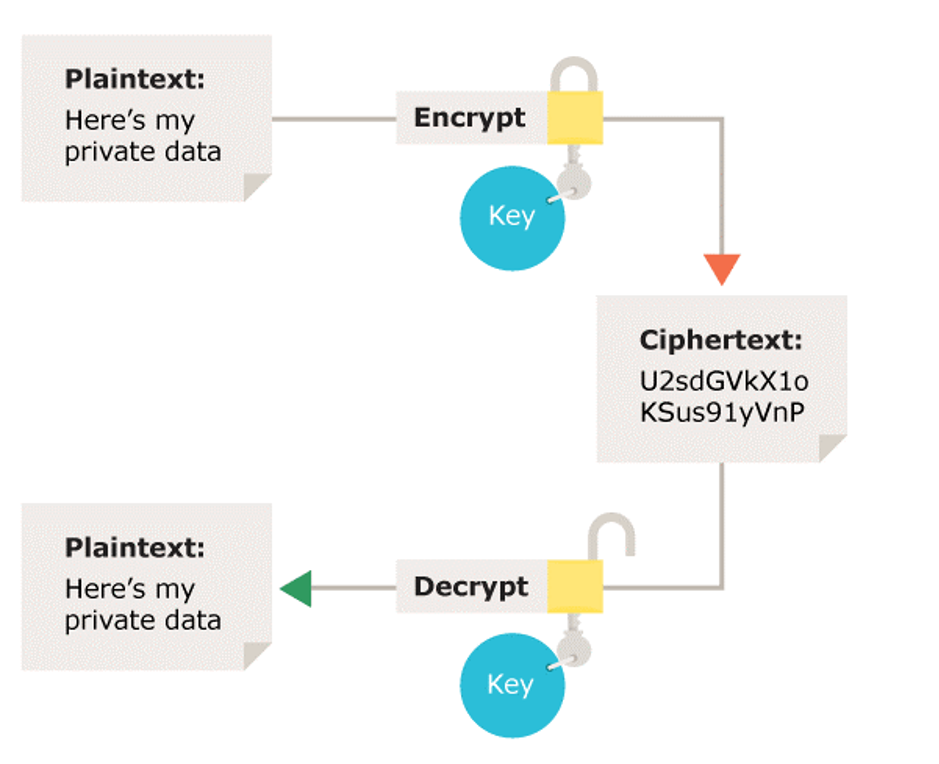
Encryption is the process of transforming readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable form (ciphertext) using algorithms and secret keys. Think of it as locking your information in a digital vault — only someone with the right key can unlock it.
Example:
Original Message: “Hello”
Encrypted Message: “Xy@#12!”
Only someone with the key can turn “Xy@#12!” back into “Hello”.
💡 Why Do We Need Encryption?
Privacy: Protects personal info like passwords, messages, and bank details.
Secure Transmission: Prevents hackers from reading data sent over the internet.
Data Safety: Makes stolen or hacked data useless without the decryption key.
🔄 Types of Encryption
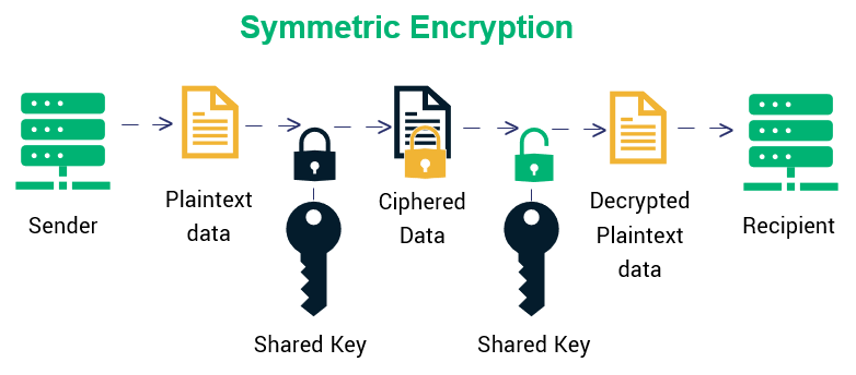
🔐 Symmetric Encryption
[Image Placeholder: Two people sharing the same key icon]
Uses the same key for encryption and decryption.
Requires both parties to share a secret key.
✅ Popular Algorithms:
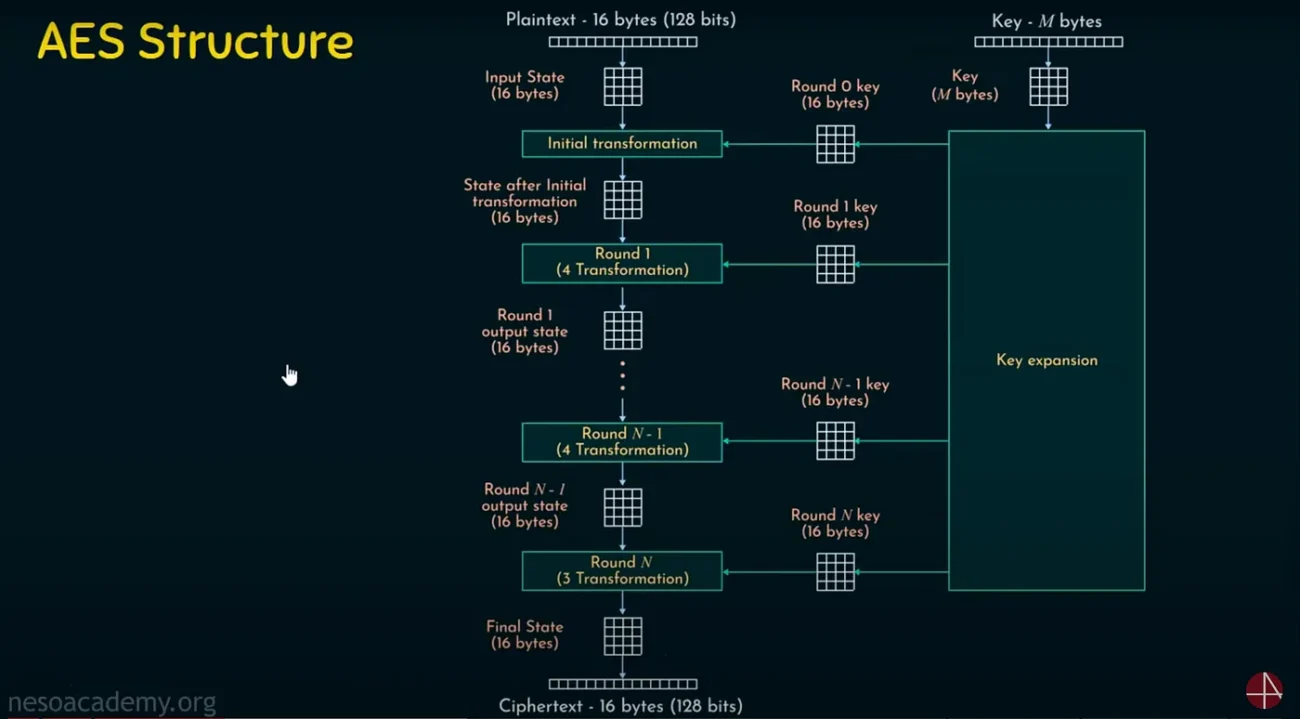
🔸 AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
Block Size: 128 bits
Key Sizes: 128, 192, or 256 bits
Used in: WhatsApp, VPNs, online banking
Strengths: Fast, secure, and globally trusted
Weakness: Requires secure key sharing
🔸 DES (Data Encryption Standard)
Block Size: 64 bits
Key Size: 56 bits
Used in: Older systems
Weakness: Can be cracked in hours – obsolete today
🔸 3DES (Triple DES)
Applies DES three times
Key Size: 112 or 168 bits
Used in: Banking (historically)
Weakness: Slower and outdated
🔸 RC4 (Rivest Cipher 4)
Type: Stream Cipher
Key Size: 40–2048 bits
Strengths: Fast, easy to implement
Weakness: Vulnerable – no longer secure
🔸 RC5 & RC6
Block Sizes: 32–128 bits
Key Sizes: up to 2040 bits
Strengths: Flexible, fast
RC6 was a finalist in the AES competition
Weaknesses: Not widely adopted, less tested
